Building Customer Trust with GDPR: A Guide for E-Commerce Brands
- February 28, 2025
- Posted by: Venkadesh Nagarajan
- Categories: Blog, E-Commerce Development
In a digital economy, data is the backbone of personalized customer experiences, targeted marketing, and seamless transactions. However, with increasing data collection comes greater responsibility, especially for digital commerce companies handling sensitive customer information. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets a global benchmark for data privacy and security, compelling businesses to adopt transparent, customer-centric data practices. Compliance is not just a legal necessity but a strategic imperative—enhancing customer trust, mitigating security risks, and positioning brands as responsible digital leaders. Non-compliance, on the other hand, can result in severe financial penalties, reputational damage, and loss of customer confidence.
For digital commerce businesses, GDPR compliance goes beyond policy updates and cookie banners; it requires a fundamental shift in data governance, security, and user control. Companies must implement privacy-by-design principles, ensuring that data collection, storage, and processing are transparent and limited to legitimate purposes. Secure authentication, encryption, and stringent access controls become essential to protect customer data from breaches. Moreover, offering consumers greater control over their data—such as the right to access, rectify, and erase personal information—can serve as a competitive differentiator. In an era where consumers are increasingly privacy-conscious, businesses that proactively embrace GDPR not only reduce regulatory risks but also build long-term customer loyalty and digital resilience. In this blog post, we’ll look at the benefits of GDPR for e-commerce companies, how to adhere to it, consequences of non-compliance, and how Navabrind IT Solutions ensures your e-commerce business is GDPR compliant.
What is GDPR?
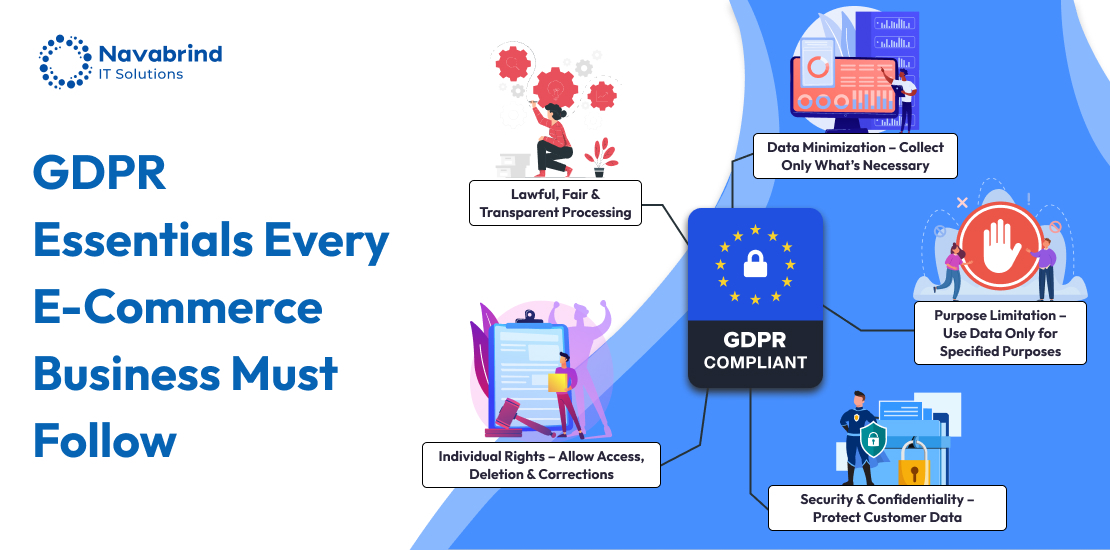
So moving on to the big questions, what is GDPR? The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive law on data privacy enacted by the EU to protect the personal data of individuals within the EU and European Economic Area (EEA). Implemented on May 25, 2018, GDPR establishes strict guidelines on how businesses collect, process, store, and share personal data, ensuring transparency and accountability. It applies to any organization, regardless of location, that handles the data of EU residents, making it a global benchmark for data privacy.
Under GDPR, businesses must obtain explicit consent from the consumer before processing personal data, provide clear information on data usage, and ensure individuals have rights such as access, rectification, and deletion of their data. Companies are also required to implement strong security measures to prevent data breaches and report any incidents of a breach within 72 hours. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, with fines reaching up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
For digital commerce businesses, GDPR is not just about legal compliance—it’s about building trust. By adopting transparent data practices, businesses can enhance customer confidence, strengthen brand reputation, and ensure long-term success in an era where data privacy is a top consumer priority.
How does GDPR impact an ecommerce business?
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) has a profound impact on e-commerce businesses, fundamentally changing how they handle customer data. Since online retailers rely heavily on data collection for marketing, sales, and customer engagement, GDPR mandates that they adopt stricter data protection measures and enhance transparency in data processing. Any e-commerce business that sells to customers within the European Union (EU), regardless of its geographical location, must comply with GDPR requirements. Failure to do so can result in hefty penalties—up to €20 million or 4% of the company’s global revenue—making compliance a critical priority.
One of the biggest changes GDPR brings to e-commerce is the requirement for explicit and informed customer consent before collecting personal data. Businesses must provide clear privacy notices, detailing how data is collected, stored, and used. Customers also have enhanced rights under GDPR, including the right to access, modify, restrict processing, or request the deletion of their data at any time. This requires e-commerce businesses to update their data policies, implement user-friendly consent mechanisms, and ensure compliance across their platforms, from websites to third-party integrations.
Security is another key focus of GDPR. E-commerce businesses must implement stringent cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, secure payment processing, and access controls, to protect sensitive customer data from breaches. In case of a data breach, businesses are required to notify regulatory authorities and affected users within 72 hours. Regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and compliance checks become essential to maintaining GDPR adherence.
Beyond legal compliance, GDPR also reshapes digital marketing practices. E-commerce businesses can no longer rely on pre-checked consent boxes or passive opt-ins for email marketing and retargeting campaigns. Instead, they must ensure customers actively opt in to receive communications, making list-building more challenging but ultimately leading to higher-quality engagement. Businesses must provide an easy way for users to withdraw consent at any time.
While GDPR poses compliance challenges, it also offers strategic benefits. Businesses that prioritize data privacy and transparency gain customer trust and loyalty. In an era where consumers are increasingly aware of data privacy concerns, GDPR-compliant e-commerce businesses can differentiate themselves as trustworthy brands, enhancing customer retention and long-term business growth.
Why is GDPR Important?
To Consumers
GDPR is crucial for consumers because it strengthens their control over personal data and enhances privacy rights. Consumers share vast amounts of data with e-commerce businesses, including personal details, payment information, and browsing behavior. GDPR ensures that businesses handle this data responsibly, requiring them to obtain explicit consent before collecting and processing it. Consumers also gain the right to access, modify, and delete their data, empowering them with greater transparency and control. GDPR mandates strict security measures to prevent data breaches, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud. By enforcing accountability on businesses, GDPR fosters consumer trust in digital transactions, making online shopping safer and more secure.
To E-commerce Businesses
GDPR is not just a legal obligation for e-commerce businesses—it’s a strategic advantage. Compliance ensures they operate within regulatory frameworks, avoiding substantial fines and reputational damage associated with non-compliance. GDPR also improves data governance by encouraging businesses to streamline data collection, storage, and processing practices, reducing inefficiencies and security vulnerabilities. Being GDPR-compliant builds customer confidence, leading to higher engagement and loyalty. In an era where data privacy concerns influence purchasing decisions, e-commerce businesses that prioritize transparency and security can differentiate themselves from competitors, ultimately driving sustainable growth and fostering long-term customer relationships.
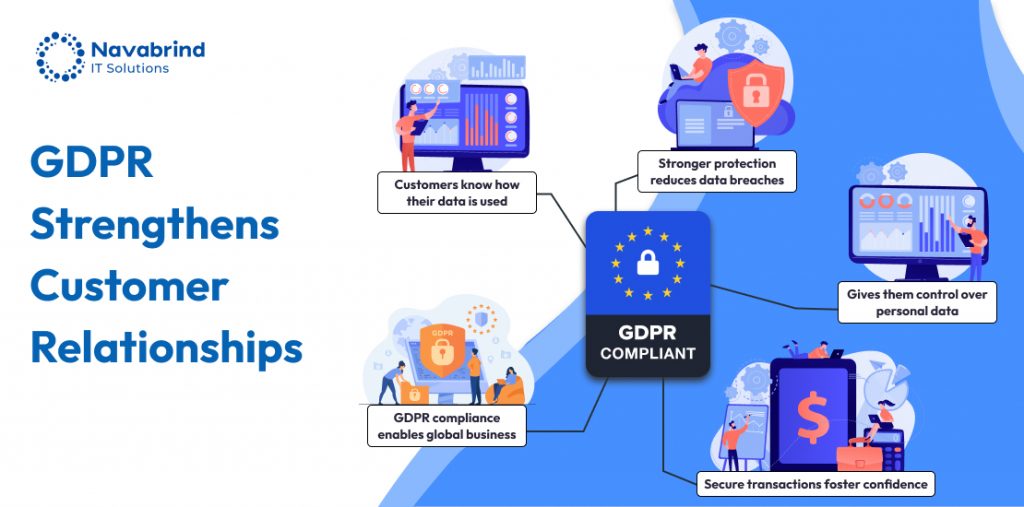
What are the Benefits of GDPR to eCommerce Stores?
- Enhanced Customer Trust and Brand Reputation
GDPR compliance demonstrates a commitment to data privacy and security, fostering trust among customers. When shoppers feel their personal data is handled responsibly, they are more likely to engage with and return to an eCommerce store, ultimately strengthening brand loyalty.
- Stronger Data Security and Reduced Risk of Breaches
GDPR mandates businesses to implement stringent security measures, such as encryption and access controls, minimizing the risk of data breaches. By securing customer data, eCommerce businesses can avoid costly cyberattacks, financial penalties, and reputational damage.
- Improved Data Management and Operational Efficiency
GDPR encourages businesses to streamline data collection and storage processes, ensuring they only retain necessary and relevant information. This reduces data clutter, enhances operational efficiency, and lowers storage and processing costs.
- Reduced Legal and Financial Risks
Non-compliance with GDPR can result in hefty fines and legal consequences. By adhering to GDPR requirements, eCommerce businesses mitigate financial risks while ensuring they meet global data protection standards, especially when serving European customers.
- Better Marketing Personalization with Consent-Driven Strategies
With GDPR’s focus on user consent, businesses can build more engaged and relevant marketing campaigns. Since customers explicitly opt in to receive communications, marketing efforts become more targeted, improving conversion rates and ROI.
- Competitive Advantage in Global Markets
Being GDPR-compliant allows eCommerce businesses to expand their reach within the European Union and beyond. Companies that prioritize data privacy and transparency stand out in global markets, positioning themselves as trustworthy and customer-centric brands.
How does an e-commerce company adhere to GDPR?
Ensuring GDPR compliance is essential for e-commerce businesses that handle the personal data of EU customers. Here’s a step-by-step approach to adhering to GDPR regulations:
- Obtain Clear and Explicit Consent
E-commerce businesses must obtain clear, informed, and specific consent from users before collecting personal data. This means:
Using opt-in checkboxes (not pre-checked) for email marketing and data collection.
Clearly stating how customer data will be used.
Allowing users to withdraw consent easily at any time.
- Implement Strong Data Security Measures
GDPR requires businesses to protect personal data from unauthorized access, breaches, and leaks. Security measures should include:
Encryption for sensitive data.
Secure payment processing with PCI-DSS compliance.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
- Provide Transparent Privacy Policies
E-commerce websites must have clear and accessible privacy policies that explain:
What data is collected and why.
How long the data is retained.
Whether data is shared with third parties.
How users can exercise their rights under GDPR.
- Enable Customer Rights Management
Under GDPR, customers have rights over their data, including: - Right to Access: Customers can request a copy of their stored data.
- Right to Be Forgotten: Users can request data deletion.
- Right to Rectification: Customers can correct inaccurate information.
- Right to Data Portability: Users can request their data in a portable format.
E-commerce businesses must have systems in place to handle these requests efficiently. - Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if Required
If an e-commerce company processes large amounts of personal data, appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) ensures GDPR compliance. The DPO oversees data protection policies, conducts audits, and serves as a point of contact for regulatory authorities. - Conduct Data Impact Assessments (DPIA)
E-commerce businesses handling sensitive customer data should conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) to identify risks and implement corrective actions to ensure GDPR compliance. - Ensure Third-Party Compliance
If using third-party services like payment gateways, CRM, or marketing tools, ensure they are GDPR-compliant. This involves reviewing contracts, data-sharing agreements, and verifying their security standards. - Report Data Breaches Within 72 Hours
If a data breach occurs, GDPR mandates businesses to report it to the relevant authorities and affected users within 72 hours. Having a breach response plan in place is crucial for compliance.
By following these steps, an e-commerce company can adhere to GDPR regulations, minimize legal risks, and build customer trust through transparent and secure data handling practices.
Consequences of Non-Compliance with GDPR
Failing to comply with GDPR can have serious legal, financial, and reputational consequences for e-commerce businesses. Here’s what non-compliance could lead to:
- Heavy Financial Penalties
GDPR imposes severe fines for violations, categorized into two levels: - Up to €10 million or 2% of global annual revenue (whichever is higher) for minor violations, such as improper record-keeping.
- Up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue (whichever is higher) for serious violations, such as failing to obtain user consent or mishandling personal data.
- Legal Consequences and Lawsuits
Non-compliance can lead to legal actions from regulatory authorities or customers. Consumers have the right to file complaints, and if their data is misused, they can take legal action, leading to compensation claims. - Data Breach Risks and Liabilities
Without GDPR-compliant security measures, businesses become vulnerable to data breaches. In the event of a breach, companies must notify authorities and affected users within 72 hours. Failure to do so can result in fines and loss of consumer trust. - Business Restrictions and Operational Disruptions
Regulatory authorities can impose temporary or permanent bans on data processing activities. This can affect business operations, including marketing campaigns, customer engagement, and international data transfers. - Reputational Damage and Loss of Customer Trust
GDPR non-compliance damages brand reputation, leading to lost customer trust and decreased sales. Modern consumers prioritize data security, and a company known for non-compliance or data breaches may struggle to attract and retain customers. - Revocation of Business Contracts and Partnerships
Many B2B clients and service providers require GDPR compliance before entering contracts. Non-compliance can lead to the loss of key partnerships and hinder business growth.
Ignoring GDPR is a high-risk decision for any e-commerce business. Investing in compliance not only avoids penalties but also fosters trust, strengthens security, and ensures sustainable growth in the digital marketplace.
Navabrind IT Solutions, is committed to ensuring compliance with the GDPR for its clients, especially those operating within the European Union. As an Odoo Gold Partner, Navabrind IT Solutions has extensive experience in implementing, integrating, customizing, migrating, and supporting ERP systems for customers across Europe, the US, the Middle East, and India.
In line with GDPR requirements, Navabrind IT Solutions emphasizes robust data protection measures. For instance, Odoo 18 offers enhanced security protocols and is designed to be GDPR-compliant, ensuring that businesses can safeguard sensitive data effectively.
It’s important to note that outsourcing to India does not automatically guarantee GDPR compliance, Navabrind IT Solutions addresses this by implementing appropriate security measures and protocols. This includes conducting thorough risk assessments, establishing comprehensive contracts, and ensuring secure data handling practices. Such measures are crucial, as the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) mandates that transferring personal data outside countries like the UK requires stringent safeguards to maintain legality.
Furthermore, with the enactment of India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) in August 2023, Navabrind IT Solutions aligns its practices to comply with both local and international data protection standards. The DPDPA shares similarities with the GDPR, focusing on the protection of digital personal data and granting individuals greater control over their information.
Navabrind IT Solutions is dedicated to upholding GDPR compliance through:
- Implementing GDPR-compliant platforms: Using sprinto/ESET like solutions with robust security features.
- Establishing comprehensive data protection protocols: Conducting risk assessments, securing contracts, and ensuring secure data handling.
- Adhering to international and local data protection laws: Aligning practices with both GDPR and India’s DPDPA.
By integrating these measures, Navabrind IT Solutions ensures that its services meet the stringent data protection requirements of clients worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.Does GDPR apply to e-commerce businesses outside the EU?
Yes, GDPR applies to any e-commerce business that offers goods or services to, or monitors the behavior of, individuals within the European Union, regardless of where the company is located. This extraterritorial reach means that even if a business operates outside the EU, it must comply with GDPR if it processes personal data of EU residents. For instance, an e-commerce store based in the U.S. or Asia that sells products to customers in France or Germany must adhere to GDPR’s strict data protection rules. The regulation ensures that EU consumers’ personal data is handled securely, with transparency, and only for legitimate purposes.
Non-compliance can have serious consequences, including fines of up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover, whichever is higher. To comply, businesses must implement clear privacy policies, obtain explicit user consent for data collection, ensure data protection by design, and provide mechanisms for users to exercise their rights, such as data access and deletion requests. Additionally, if an international e-commerce business processes large amounts of EU personal data, it may need to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) or a representative within the EU. Therefore, even non-EU businesses must carefully assess their operations to ensure GDPR compliance and avoid legal risks.
2. What constitutes ‘personal data’ under GDPR in an e-commerce context?
Under GDPR, personal data refers to any information that can directly or indirectly identify an individual. In an e-commerce context, this includes common identifiers such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, and home or billing addresses. It also extends to digital identifiers such as IP addresses, device IDs, cookies, and browsing behavior, as these can be used to track and profile users. Payment details, including credit card numbers and transaction histories, are also considered personal data since they link to an individual’s financial activities. GDPR ensures that e-commerce businesses handle this data with care, providing transparency and accountability in its collection and processing.
Beyond basic customer details, GDPR also protects “special category” data, such as biometric identifiers, health information, or any other sensitive details that could be misused for discrimination. E-commerce businesses must implement strong security measures like encryption, pseudonymization, and access controls to safeguard personal data. Additionally, they must provide clear privacy policies, obtain explicit consent where necessary, and allow users to request data deletion or correction. Given the rise of AI-driven personalized shopping experiences, companies must be particularly cautious about how they track user behavior and leverage data analytics to ensure compliance with GDPR regulations.
3. Is explicit consent required for all data processing activities in e-commerce?
Not always. While explicit consent is one of the key lawful bases for processing personal data under GDPR, it is not required for every data processing activity in e-commerce. GDPR outlines six legal bases for processing data: consent, contract performance, legal obligation, vital interests, public task, and legitimate interest. For instance, if an online store collects a customer’s shipping address and payment details to fulfill an order, this falls under contract performance, meaning explicit consent is not required. Similarly, if an e-commerce business is legally required to store financial transaction records for tax compliance, the legal obligation basis applies.
However, explicit consent is necessary when processing sensitive data or when using personal data for marketing, profiling, or tracking user behavior beyond what is necessary for service delivery. For example, if an e-commerce business wants to send promotional emails, use third-party tracking cookies, or share customer data with advertising networks, it must obtain clear and affirmative user consent. Businesses must ensure consent is freely given, informed, specific, and revocable at any time. They should also provide clear privacy policies and consent management tools to allow users to control their data preferences, ensuring compliance with GDPR regulations.
4. How should e-commerce businesses handle data breach notifications under GDPR?
Under GDPR, e-commerce businesses must act swiftly in the event of a data breach that poses a risk to individuals’ rights and freedoms. If a breach occurs, companies are required to notify the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours of becoming aware of it. This notification should include the nature of the breach, the type and volume of affected data, the potential impact on individuals, and the corrective actions being taken. If the breach is likely to result in significant harm—such as identity theft, financial loss, or reputational damage—businesses must also inform affected customers promptly. This communication should be clear, transparent, and provide guidance on how individuals can protect themselves.
To minimize the risk of breaches and ensure compliance, e-commerce businesses must implement robust security measures, such as data encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. They should also have an incident response plan in place, outlining steps for detecting, containing, and mitigating breaches. Regular security audits and staff training on data protection best practices can further strengthen a company’s ability to handle data breaches effectively. By prioritizing strong security and transparency, e-commerce businesses can build trust with customers while ensuring compliance with GDPR’s strict data protection requirements.
5.What are the penalties for non-compliance with GDPR for e-commerce companies?
Non-compliance with GDPR can lead to severe financial and reputational consequences for e-commerce businesses. The regulation imposes two tiers of fines based on the nature and severity of the violation. Minor infractions, such as improper record-keeping or failing to notify authorities of a data breach within 72 hours, can result in fines of up to €10 million or 2% of the company’s global annual revenue—whichever is higher. More serious violations, including unlawful data processing, failure to obtain proper user consent, or compromising users’ rights and freedoms, can lead to fines of up to €20 million or 4% of the company’s global annual revenue. These penalties are designed to ensure businesses take data protection seriously and implement necessary compliance measures.
Beyond financial repercussions, non-compliance can also damage an e-commerce company’s reputation, eroding customer trust and leading to a loss of business. Companies found in violation may face lawsuits, increased scrutiny from regulators, and restrictions on data processing activities, which can impact operations significantly. Additionally, a publicized data breach or compliance failure can deter customers from engaging with the brand, leading to long-term revenue losses. To mitigate these risks, e-commerce businesses must implement robust data protection policies, regularly update security measures, and ensure they meet GDPR requirements in handling customer data.
6. Are e-commerce businesses required to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)?
E-commerce businesses are required to appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) under GDPR if their core activities involve large-scale processing of sensitive personal data or systematic monitoring of individuals. This includes businesses that track user behavior across websites, process financial or health-related data, or engage in large-scale profiling for personalized marketing. A DPO’s primary role is to ensure GDPR compliance, monitor data processing activities, provide guidance on data protection policies, and serve as a point of contact between the company and regulatory authorities. The DPO must have expert knowledge of data protection laws and work independently to uphold GDPR principles.
Even if an e-commerce business is not legally required to appoint a DPO, having one can be beneficial. A dedicated DPO can help businesses navigate the complexities of GDPR, conduct risk assessments, and implement best practices to prevent data breaches and regulatory violations. For smaller companies, outsourcing the DPO function to an external expert is a viable option. Regardless of whether a DPO is appointed, e-commerce businesses must ensure that their data protection responsibilities are clearly defined, with a structured approach to compliance, security, and risk management.
Schedule a conversation with us now!
Venkadesh Nagarajan
Related Articles
-
Post
Odoo ERP for the Retail Industry: Driving Efficiency and Growth
Odoo ERP for the Retail Industry: Driving Efficiency and Growth February 27, 2026 Posted by: Vasanth Anantharaman Categories: Blog, Odoo for Retail industry No Comments Why the Retail Industry Runs Better on Odoo ERP Retail runs on dozens of disconnected apps. One tool for sales, another for stock, a third for loyalty. None speak to -
Post
From Formula to Forecast: Odoo’s Transformative Edge in Chemical Manufacturing
From Formula to Forecast: Odoo’s Transformative Edge in Chemical Manufacturing February 27, 2026 Posted by: Jaishree Jayabal Singh Categories: Blog, Odoo ERP for Chemical Industry No Comments Odoo ERP for Chemical Industry Solves the Disconnection Problem Chemical manufacturing operates across multiple fronts, production floors, warehouse storage, laboratory testing, and regulatory reporting. Managing these as isolated -
Post
How Odoo ERP Helps Manufacturers Track Machine Efficiency and Move Toward Industry 4.0
How Odoo ERP Helps Manufacturers Track Machine Efficiency and Move Toward Industry 4.0 February 25, 2026 Posted by: Venkadesh Nagarajan Category: Uncategorized No Comments The Shift Toward Smart Manufacturing Machine efficiency is the core of manufacturing. Without it, cost control and scalability are impossible. Industry 4.0 accelerates this, merging IoT and data analytics to drive
How can we help you?
Get in touch with a solutions consultant that can share best practices and help solve specific challenges.