Enhancing Manufacturing Quality: An In-Depth Look at the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
- July 3, 2024
- Posted by: Tony
- Categories: Blog, PPAP

The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is a quality assurance tool in manufacturing, ensuring equipment parts meet stringent standards before mass production. This blog post explores the intricacies of PPAP, its critical role in manufacturing, its widespread applications across various industries, and steps in the implementation of a PPAP solution. Discover how PPAP drives quality, consistency, and customer confidence in today’s competitive market.
In the manufacturing sector, quality assurance is paramount. One of the critical tools used to ensure the quality and consistency of parts and components is the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP). PPAP is an essential element in the manufacturing industry, serving as a standardized procedure to ensure that suppliers meet the necessary quality requirements before mass production begins. This blog post delves into PPAP, its purpose and importance, and its applications across various industries.
Understanding PPAP: What Exactly is PPAP, and What Does it Entail?
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is a standardized process used in the automotive and other manufacturing industries to ensure that a supplier’s production process can consistently produce parts that meet all customer requirements. Initially developed by the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG), PPAP has become a critical part of the quality management systems for many manufacturers.
Aspects of the Production Part Approval Process
Production Part Approval Process involves several key elements, typically documented in a PPAP submission package, which include:
- Design Records: Detailed drawings and specifications of the part or component.
- Authorized Engineering Change Documents: Any documents showing approved changes to the design records.
- Engineering Approval: Evidence that the part has been approved by the engineering team.
- Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA): A risk management tool to identify potential failures in the design phase.
- Process Flow Diagram: A detailed map of the manufacturing process, from raw materials to finished product.
- Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA): A risk management tool used to identify potential failures in the manufacturing process.
- Control Plan: A detailed plan outlining how the production process will be controlled to ensure quality.
- Measurement System Analysis (MSA): Studies to ensure that the measurement systems used are accurate and reliable.
- Dimensional Results: Data showing that the part meets all specified dimensions.
- Material, Performance Test Results: Evidence that the part meets all material and performance specifications.
- Initial Process Studies: Data from initial production runs to show that the process can produce parts within specifications.
- Qualified Laboratory Documentation: Certification that all testing was performed by qualified laboratories.
- Appearance Approval Report (AAR): Approval of the part’s appearance, where applicable.
- Sample Production Parts: Samples of parts produced during the PPAP run.
- Master Sample: A sample part retained for comparison with future production.
- Checking Aids: Tools used to check the parts during production.
- Customer-Specific Requirements: Any additional requirements specified by the customer.
- Part Submission Warrant (PSW): A summary document signed by the supplier to certify that all PPAP requirements have been met.

Why is PPAP Critical in Manufacturing, and What are the Benefits of Implementing PPAP?
The primary purpose of the Production Part Approval Process is to ensure that all customer engineering design records and specification requirements are correctly understood by the supplier. And that the supplier can produce a product consistently at specified requirements during the actual production run at the quoted production rate.
Key Benefits of Implementing PPAP:
- Quality Assurance: PPAP ensures that parts meet all specified quality requirements before they are shipped to the customer. This prevents defective parts from reaching the assembly line or the end consumer.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying design and process failures early through DFMEA and PFMEA, PPAP mitigates risk. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of costly recalls and rework.
- Consistency and Reliability: PPAP requires suppliers to demonstrate that their manufacturing processes can produce parts consistently. This consistency is crucial for maintaining product reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Customer Confidence: PPAP provides customers with the assurance that their suppliers can meet their requirements consistently. This builds trust and strengthens supplier-customer relationships.
- Continuous Improvement: The PPAP process encourages continuous improvement by requiring suppliers to review and update their processes and quality control measures.
Which Industries Commonly Use PPAP, and for What Types of Products or Components is it Relevant?
While PPAP originated in the automotive industry, its principles and methodologies have been adopted by various sectors due to its effectiveness in ensuring quality and consistency.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, PPAP ensures that all parts and components meet stringent safety and performance standards. It is used for a range of parts, from simple fasteners to complex assemblies like engines and transmissions. Given the high stakes of automotive manufacturing, where failures can result in significant safety issues, PPAP is indispensable.
Aerospace Industry
Given the rigorous standards for safety and performance in aerospace, PPAP helps manufacturers maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and ensures that all parts are fit for use in critical applications.
Consumer Goods
Manufacturers of consumer goods, particularly those involving complex electronics and appliances, use PPAP to ensure that their products meet quality standards before beginning mass production. PPAP is particularly relevant for companies producing high-volume items where consistency and reliability are key to maintaining brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
Medical Devices
The medical device industry relies on PPAP to ensure that components and assemblies meet stringent regulatory requirements. Given the critical nature of medical devices, ensuring that all parts are produced consistently to high-quality standards is essential for patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Industrial Equipment
Manufacturers of industrial machinery and equipment use PPAP to ensure that their parts and assemblies meet the necessary quality and performance standards. This is important for maintaining the reliability and efficiency of industrial operations, where equipment failures can result in downtime and costs.
Electronics
In the electronics industry, PPAP helps manufacturers ensure that all components, from circuit boards to semiconductor devices, meet quality standards. This is important given the complexity and precision required in electronics manufacturing.

Implementing a Production Part Approval Process Solution
While the PPAP is needed across industries, implementing and maintaining a robust solution involves several key steps. These steps will be followed by your technology partner implementing your PPAP solution, or by your internal IT team. Here is a detailed outline of the process:
Planning Phase
- Understand the Requirements:
- Understand the Need: Thoroughly understand the features required and to be implemented.
- Customer-Specific Requirements: Identify any additional requirements specific to the customer.
- Assemble a Team:
- Cross-Functional Team: Form a team with members from quality, engineering, manufacturing, and supply chain departments.
- Assign Roles: Clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each team member.
- Develop a PPAP Plan:
- Timeline: Create a detailed timeline for the PPAP submission, including milestones and deadlines.
- Resource Allocation: Identify and allocate the necessary resources, including personnel, equipment, and budget.
Execution Phase
- Design Documentation:
- Design Records: Ensure that all design records, including drawings, specifications, and material requirements, are complete and up-to-date.
- Engineering Change Documentation: Document any changes made to the design since the last submission.
- Process Flow Diagram:
- Visual Representation: Create a process flow diagram that visually represents the range of manufacturing processes.
- Identify Steps: Identify each step in the process, from receiving raw materials to shipping the final product.
- Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA):
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a PFMEA to identify and assess potential risks and their impacts on the process.
- Mitigation Plans: Develop mitigation plans for each identified risk.
- Control Plan:
- Control Methods: Develop a control plan that outlines the control methods for each step of the process.
- Measurement Systems: Define the measurement systems and inspection criteria to ensure product quality.
- Measurement System Analysis (MSA):
- Gauge R&R Studies: Conduct Gauge Repeatability and Reproducibility (R&R) studies to validate the measurement systems.
- Calibration Records: Ensure that all measurement equipment is calibrated and documented.
- Process Capability Study:
- Capability Index: Perform process capability studies to determine the capability indices (Cp, Cpk) for critical characteristics.
- Data Analysis: Analyze the data to ensure the process can handle production within specification limits.
- Initial Sample Inspection Report (ISIR):
- Sample Parts: Produce initial sample parts and perform detailed inspections to verify conformance to specifications.
- Documentation: Document the results of the inspections and include them in the ISIR.
- Production Trial Run:
- Pilot Production: Conduct a pilot production run to validate the process and identify potential issues.
- Data Collection: Collect data during the trial run and analyze it to ensure consistency and quality.
- Submit PPAP Package:
- Compile Documentation: Compile all the required documentation, including design records, PFMEA, control plan, MSA, capability study, ISIR, and other relevant documents.
- Customer Submission: Submit the PPAP package to the customer for review and approval.
Maintenance Phase
- Ongoing Monitoring:
- Process Monitoring: Continuously monitor the manufacturing process to ensure it remains in control and capable.
- Regular Audits: Conduct internal audits to verify compliance with the control plan and PPAP requirements.
- Change Management:
- Document Changes: Document any changes to the design, process, or materials and evaluate their impact on the PPAP.
- Re-Submission: If significant changes are made, prepare and submit an updated PPAP package for approval.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop to collect and analyze data from production and customer feedback.
- Improvements: Implement continuous improvement initiatives to enhance process efficiency and product quality.
- Training and Education: Ensure team members are adequately trained in PPAP requirements and procedures.
- Communication: Maintain clear and consistent communication with the customer throughout the PPAP process.
- Documentation Control: Implement a robust system to manage and track all PPAP-related documents.
To summarize, PPAP is a vital process in the manufacturing industry, ensuring that parts and components meet stringent quality standards before they enter mass production. By providing a comprehensive framework for quality assurance, risk mitigation, and continuous improvement, PPAP helps manufacturers deliver consistent, reliable products to their customers. Its application across various industries, from automotive to medical devices, underscores its versatility and importance in maintaining high standards of quality and performance. As manufacturing continues to evolve, the role of PPAP in ensuring product quality and customer satisfaction will only become more critical.
If you would like to integrate PPAP with your Odoo ERP, please reach out to Navabrind IT Solutions. We have extensive experience implementing, customizing, and maintaining digital commerce solutions. We would be happy to give you a free consultation on the benefits of empowering your manufacturing process with PPAP. Email us at [email protected] to schedule a call.
Schedule a conversation with us now!
Related Articles
-
Post
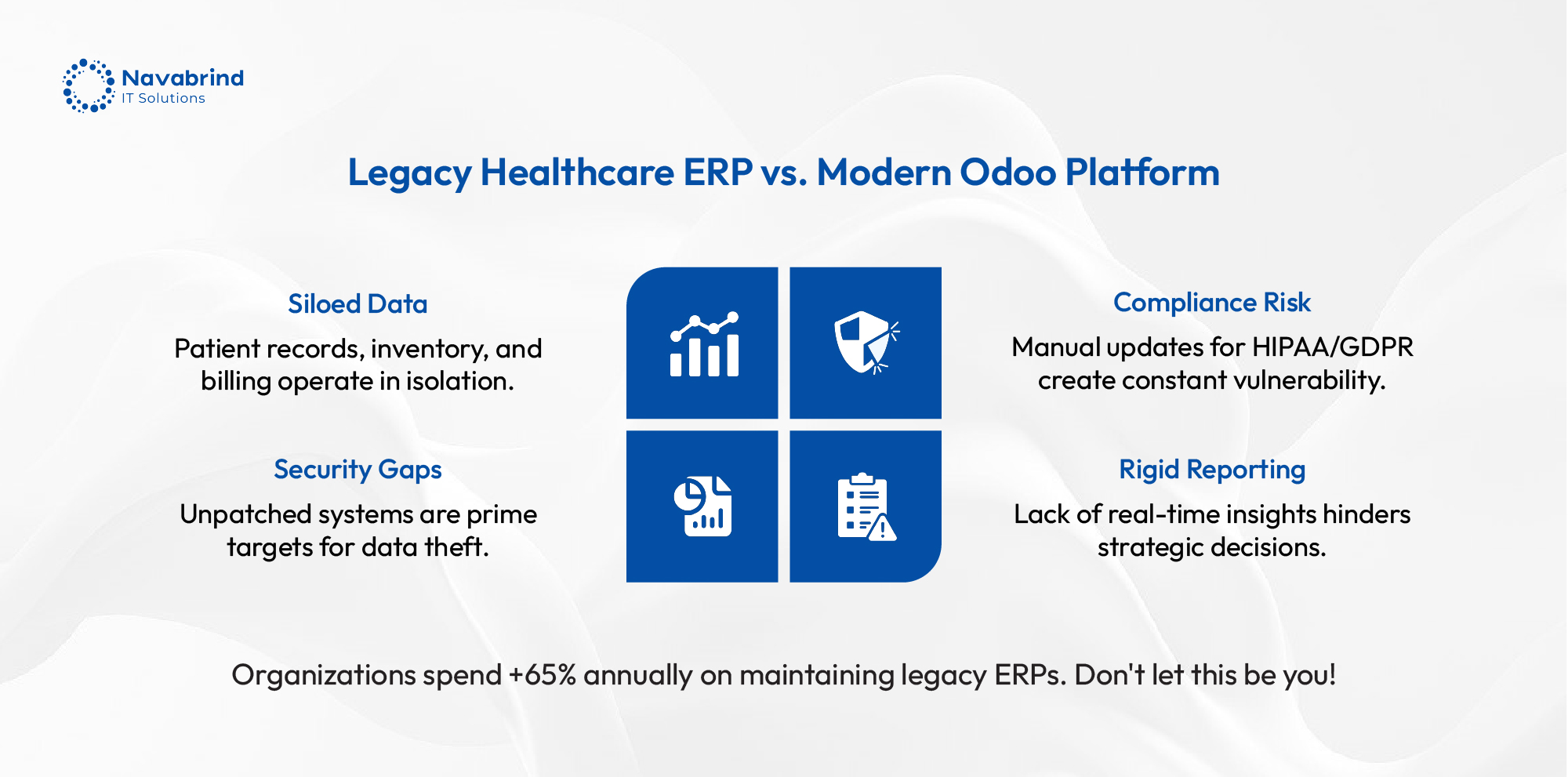
From Legacy Healthcare ERP to Odoo ERP: Why You Need Expert Odoo Migration Help
From Legacy Healthcare ERP to Odoo ERP: Why You Need Expert Odoo Migration Help February 11, 2026 Posted by: Tony Category: Uncategorized No Comments Why Healthcare Organizations Need Odoo ERP Migration Legacy healthcare ERP systems create barriers to efficiency. They are expensive to maintain, and struggle to integrate tools. This disconnect impacts patient care coordination, -
Post
From LLMs to Agentic AI: A Practical Guide to What They Mean and How to Choose
From LLMs to Agentic AI: A Practical Guide to What They Mean and How to Choose February 4, 2026 Posted by: Tony Categories: Artificial Intelligence, Blog No Comments As definitions, use cases, expectations, and investments around Large Language Models (LLMs), Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), AI agents, and agentic AI continue to expand, many individuals and organizations -
Post
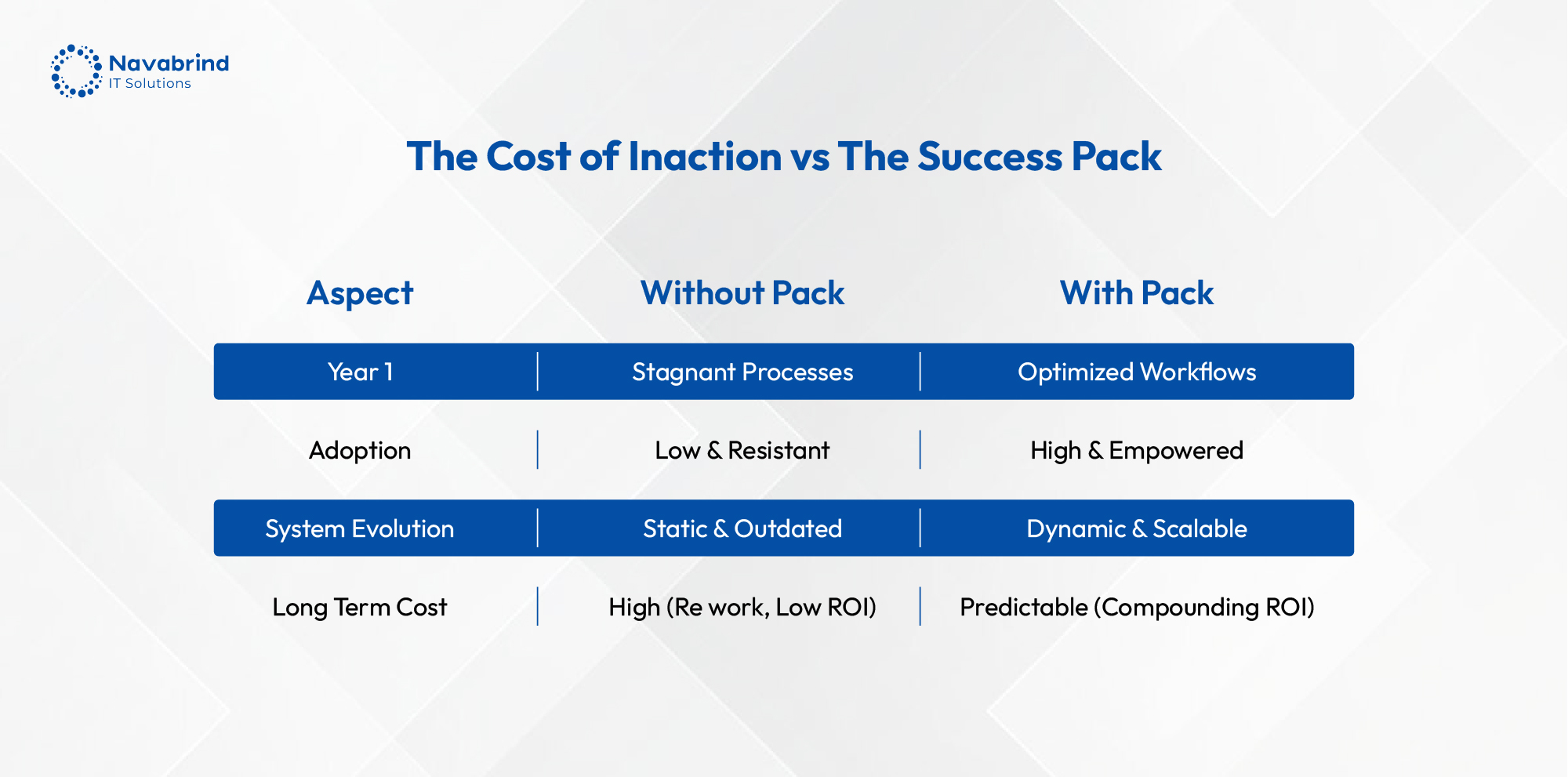
Beyond Go-Live: How Your Odoo Success Pack Drives Real, Long-Term ROI
Beyond Go-Live: How Your Odoo Success Pack Drives Real, Long-Term ROI February 3, 2026 Posted by: Category: Uncategorized No Comments The Implementation Myth Businesses mistakenly measure ERP success by completing the implementation phase while the actual measure of value is the operational transformation unlocked after go-live. The Odoo Success Pack is the framework engineered to
How can we help you?
Get in touch with a solutions consultant that can share best practices and help solve specific challenges.